M1-like macrophage exosomes with OX40L overexpressed for cancer immunotherapy

M1-like macrophage exosomes with OX40L overexpressed for cancer immunotherapy
Cancer is still one of the main factors threatening human life and health safety. Although current immunotherapy represented by PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors has achieved great success, patients' benefit is limited. Developing new immunotherapies may be one of the directions to solve the current cancer treatment dilemma.
Recently, researchers from several institutes including the Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Sun Yat sen University, China published an original research paper entitled "OX40L-expressing M1-like macrophage exosomes for cancer immunotherapy" on Journal of controlled release (JCR Q1 IF:10.8). In this study, EGFP-OX40L overexpressing stable cells constructed by Ubigene were used to develop a novel engineered M1-like macrophage exosomeOX40L M1-exos for cancer immunotherapy.
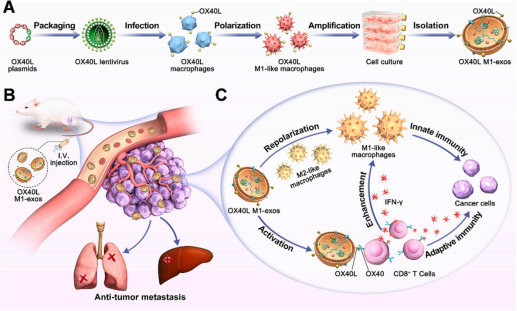
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the preparation of the OX40L M1-exos and its anticancer effect
In this study, the researchers developed the M1-like macrophage exosomes with overexpressing OX40L: OX40L M1-exos using biotechnology including gene-related cell engineering. OX40L M1-exos can activate T cell-mediated adaptive immunity through OX40/OX40L pathway; and can reprogram M2-like tumor-associated macrophages into M1-like macrophages, thereby restoring and enhancing macrophage-mediated innate immunity. In animal models, OX40L M1-exos effectively achieved the synergistic effect of innate and adaptive immunity, significantly inhibited the growth and spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer in mice, and prolonged the survival of mice.
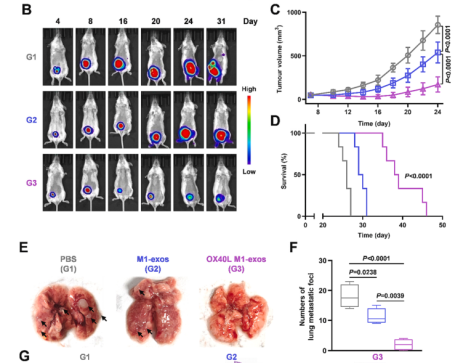
Figure 2. Evaluation of the effect of inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis in vivo
In addition, OX40L M1-exos is also used as a drug loading platform for drug delivery, providing a platform and method for combined therapy with other drugs (such as some small molecule drugs). In conclusion, OX40L M1-exos provides a novel and effective strategy for tumor immunotherapy.


