CRISPR Library Plasmid
CRISPR library plasmid is a high-throughput screening tool developed based on the CRISPR–Cas9 system. By cloning genome-wide sgRNA expression cassettes into a standardized vector, a pooled plasmid library capable of simultaneously targeting a large number of genes is constructed. After packaging the CRISPR library plasmid into lentiviral particles and delivering it into cells, combined with deep sequencing and phenotypic analysis, it enables systematic elucidation of gene functional networks, drug targets, and pathogenic mechanisms.
Why choose Ubigene?
Why choose Ubigene?
Comprehensive In-Stock Selection
Proprietary sgRNA Design Tool
Comprehensive Quality Control with Full Traceability
Customized CRISPR Library Plasmids to Meet Diverse Research Needs
High-Capacity sgRNA Library Customization for Broader Coverage
Proprietary High-Efficiency Competent Cells to Minimize Amplification Errors
Services Overview
In-Stock CRISPR Library Plasmids
Electroporation-based amplification of CRISPR library plasmids, followed by NGS sequencing to assess sgRNA coverage and uniformity.
Turnaround
1 week
Deliverables
CRISPR Library plasmids, NGS sequencing report
CRISPR Library Plasmid Modification
Customized modification of CRISPR library plasmid, transferring sgRNA sequences from a specific library into the new vector, with NGS sequencing to ensure sgRNA coverage and uniformity.
Turnaround
4-6 weeks
Deliverables
CRISPR Library plasmids, NGS sequencing report
CRISPR Custom Library Plasmids
Construction of new CRISPR library plasmids, including sgRNA design, chip-based synthesis, vector construction, plasmid electroporation and amplification, and NGS quality control.
Turnaround
7-9 weeks
Deliverables
CRISPR Library plasmids, NGS sequencing report
Workflow and Validation
sgRNA Design
Chip-Based Synthesis
Vector Construction
Competent Cell Preparation
CRISPR Library Plasmid Electroporation
Large-Scale Library Plasmid Amplification
Restriction Enzyme Verification
NGS Sequencing
Case Studies
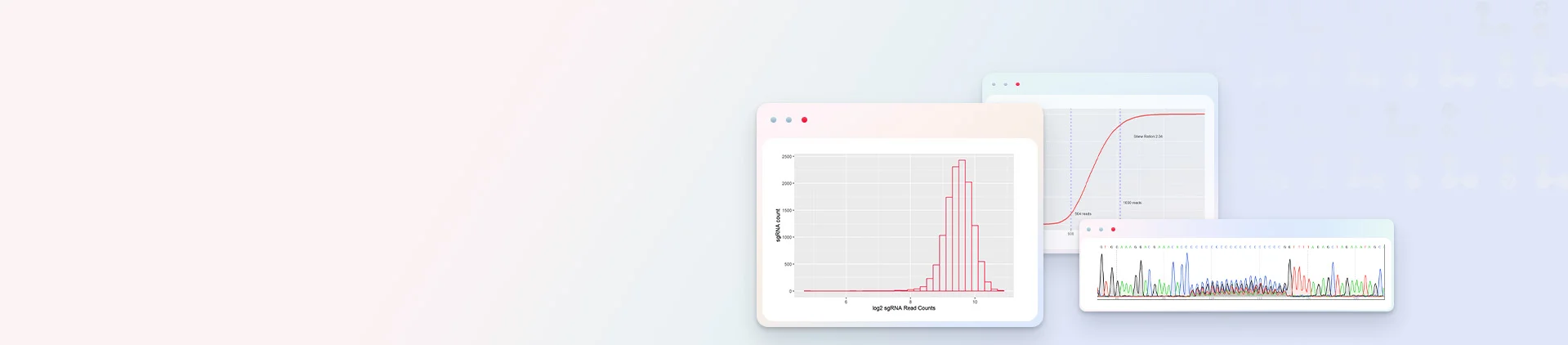
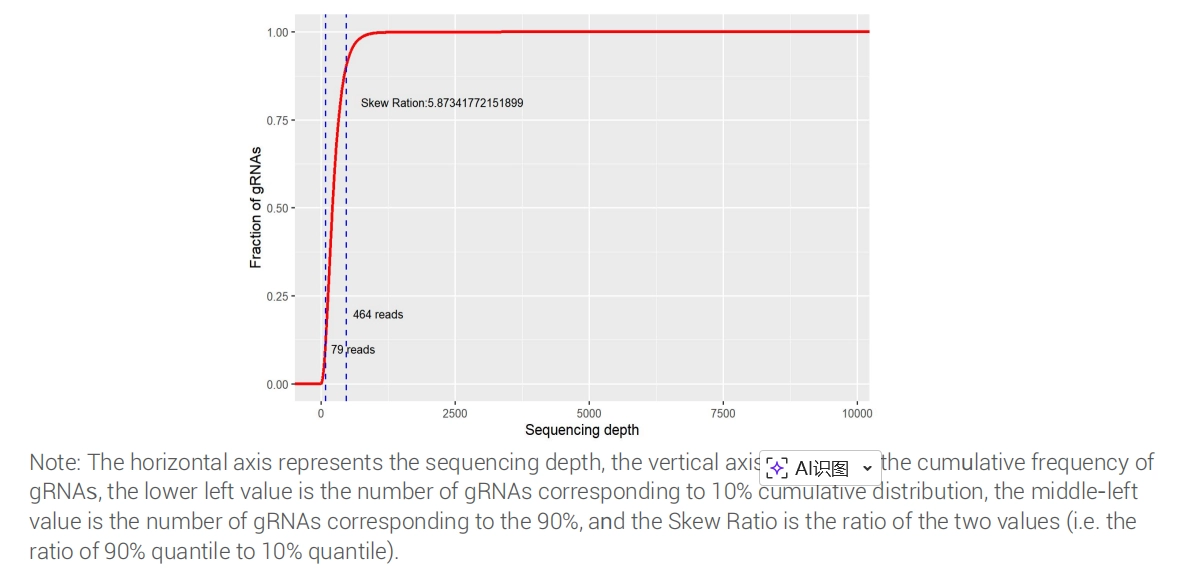
NGS Sequencing Results for Customized CRISPR Library plasmid
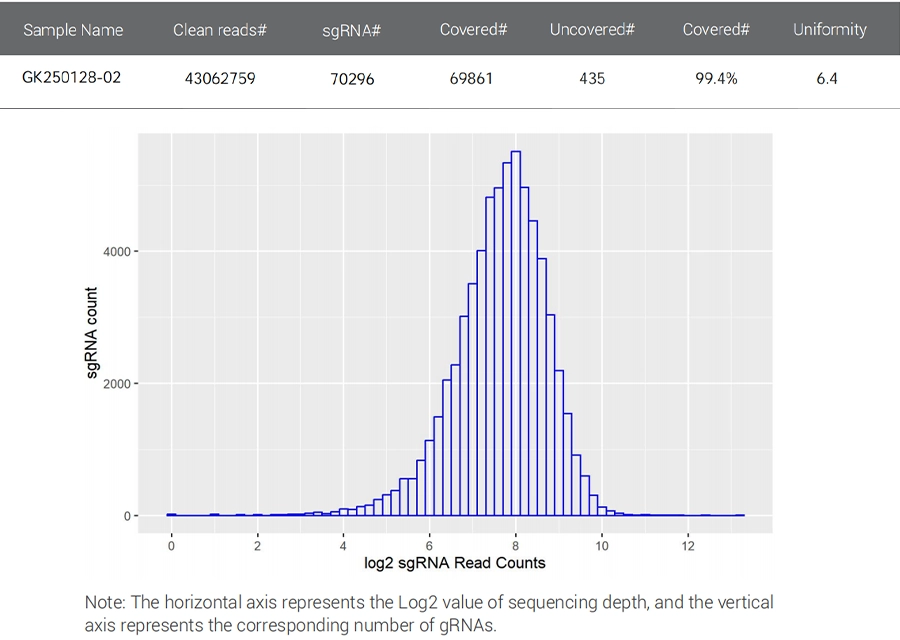
View Picture
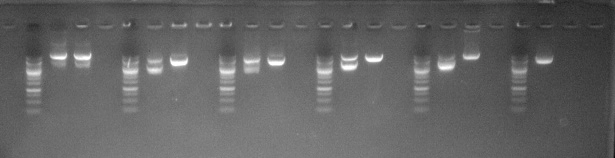
View Picture
Independently developed competent cells enable high-efficiency plasmid amplification with minimal recombination and no noticeable abnormal bands.
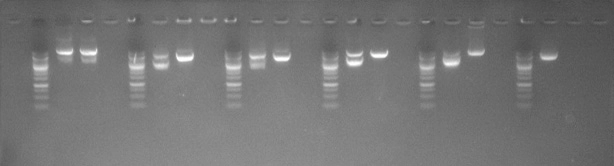
View Picture
Restriction Enzyme Analysis Combined with Sanger Sequencing to Ensure CRISPR Library Plasmids Are Free of Other Vector Contaminations.
View Picture
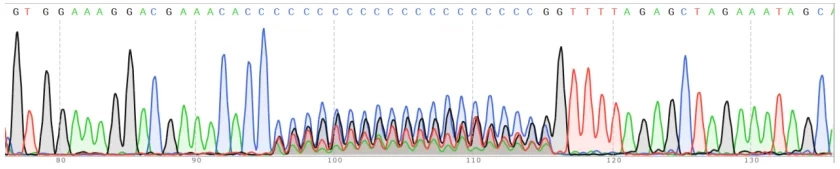
View Picture
FAQs
1. How to detect the coverage and uniformity of sgRNA in library plasmids?
By using NGS, you can comprehensively evaluate the coverage and uniformity of sgRNA in your library plasmids, ensuring high-quality and reliable CRISPR screening results.
2. Information Required from Customers for Library Screening Projects
1) Screening Objectives and Experimental Goals
- a) Define the screening type: positive selection / negative selection
- b) Specify the pathway, phenotype, function, or target of interest (e.g., cell proliferation, drug resistance, apoptosis, migration, etc.)
2) Cell Line Information
- a) Cell line name, source, adherence properties, and growth characteristics
- b) Whether the cell line stably expresses Cas9
- Transduction efficiency and antibiotic sensitivity (e.g., effective puromycin concentration range)
3) Library Selection Preferences (if applicable)
- a) Whole-genome CRISPR library / pathway-focused CRISPR library / custom CRISPR library
- b) Whether a target gene list is already available, or Ubigene assistance is needed for library design
4) Screening Strategy and Treatment
- a) Screening method (e.g., compound treatment, passaging, flow cytometry sorting, in vivo screening)
- b) Screening duration and enrichment time points (e.g., 2 weeks, 4 weeks, etc.)
5) Downstream Sequencing and Data Analysis
- a) Ubigene can provide NGS sequencing and enrichment analysis (e.g., MAGeCK analysis, etc.)
6) Additional Requirements (if any)
- a) Multiple-round screening or replicate experiment designs
- b) Setup of specific positive/negative controls
If you have not yet finalized the experimental design, Ubigene offers one-on-one project customization services to help optimize the screening strategy and CRISPR library selection. Get in touch with our experts now
3. Principle of CRISPR Library Screening
CRISPR library screening is a high-throughput functional genomic technique that enables systematic knockout, activation, or inhibition of nearly every gene in the genome. By introducing a pooled library containing thousands to tens of thousands of different sgRNAs into a population of cells, each cell receives a unique genetic perturbation. Under a defined selection pressure (such as compound treatment or flow cytometry-based sorting), cells carrying sgRNAs that confer a particular phenotypic advantage or disadvantage will become enriched or depleted over time. Subsequent next-generation sequencing (NGS) is used to quantify changes in sgRNA abundance, allowing identification of key regulatory genes involved in the biological process of interest.
4. Workflow of CRISPR Library Screening
1) Selection of an Appropriate Cell Model
- a) The cell line should stably express Cas9 or dCas9 (for knockout, activation, or interference applications)
- b) Cells must be susceptible to viral transduction, capable of sufficient passaging, and tolerant to screening conditions (e.g., compound treatment, hypoxia, etc.)
2) CRISPR Library Construction and virus Packaging
- a) Select an appropriate sgRNA library — whole-genome, pathway-specific, or custom-designed.
- b) Construct the library plasmid pool and package it into lentiviral particles, ensuring high-quality and low-bias delivery into cells.
3) Transduction and CRISPR Library Cell Pool construction
- a) Infect target cells at a low multiplicity of infection (MOI) to ensure each cell carries only one sgRNA.
- b) construct a cell pool with sufficient library coverage, typically > 300* to 500*.
4) Application of Selection Pressure
- a) Apply specific selection conditions to the infected cell pool (e.g., compound treatment, serial passaging, flow cytometry sorting)
- b) Set up treatment and control groups for enrichment-based screening.
5) Genomic DNA Extraction and NGS Sequencing
- a) Extract genomic DNA (gDNA) from cells and PCR-amplify the sgRNA barcode region.
- b) Perform high-throughput sequencing (NGS) to quantify changes in sgRNA abundance before and after screening.
6) Bioinformatics Analysis and Hit Gene Identification
- a) Analyze data using tools such as MAGeCK or edgeR to identify enriched or depleted sgRNAs.
- b) Determine candidate key genes and perform functional validation in follow-up experiments.
5. Why Choose Ubigene for CRISPR Library Screening?
- 1) Reliable and Scalable Cell Biology Platform
Ubigene offers diverse phenotypic analysis platforms that support a wide range of functional screening systems. Our capabilities fully cover compound and viral treatments, serial passaging, co-culture assays, flow cytometry sorting, cell migration and adhesion assays, and in vivo screening, enabling flexible and robust experimental designs. - 2) Reliable and Scalable Cell Biology Platform
Our well-established cell biology platform meets the demands of large-scale cell culture. With extensive experience in handling various cell systems, our technical team ensures stable and reproducible performance across multiple screening models. - 3) End-to-End, Streamlined Screening Services
Ubigene provides a fully integrated and quality-controlled workflow, including pilot optimization, large-scale screening, and downstream analysis. We offer a one-stop CRISPR screening solution, seamlessly connecting every stage of the workflow to ensure continuity, efficiency, and high success rates. - 4) Expert Technical Support
Our technical team brings deep expertise in functional genomics and screening system development. We provide hands-on guidance throughout experimental design and implementation, ensuring scientifically sound and efficient execution.