Commonly Used Cell Models and Applications in Immunological Research

Commonly Used Cell Models and Applications in Immunological Research

The immune system, composed of immune organs, cells, and active factors, plays a crucial role in immune surveillance, defense, and regulation. It serves as a vital defense mechanism against pathogens (such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites) and abnormal cells (such as cancer cells). Some hotspots in immunological research include immunotherapy (e.g., cancer immunotherapy, treatment of autoimmune diseases), inflammasomes, and vaccine development [1]. Researchers often employ various in vitro cell models to study immune system diseases and mechanisms. This article introduces several commonly used cell lines in immunological research and their applications in gene editing.
Contents
Human Monocytic Cell Line (THP-1)
(Catalog No: YC-D011)
Source: THP-1 cells are a monocytic cells isolated from the peripheral blood of a patient with acute monoblastic leukemia.
Characteristics: THP-1 cells phagocytose latex particles and sensitized red blood cells, lack immunoglobulins, but express C3R and FcR. They have monocyte surface markers (e.g., CD14) and can differentiate into macrophage-like cells under PMA stimulation to mimic in vivo immune responses. These cells have simple culture conditions, rapid proliferation, are suitable for large-scale experiments and drug screening, and are amenable to transfection. They are widely used in studies of inflammation, immune regulation, cancer, infectious diseases, and drug toxicity assessment.
Application Case 1[2]: Researching the activation mechanism of the NLRP3 inflammasome is significant for understanding the development of inflammatory diseases. Using the THP-1 cell line as a model, researchers found that heat-killed (HK) bacteria are a singular stimulus for the NLRP3 inflammasome in THP-1 cells, leading to the release of appropriate levels of IL-1β. Knocking out NLRP3 in THP-1 cells demonstrated that the absence of NLRP3 inhibited the cleavage of Caspase-1 and the release of mature IL-1β after HK bacterial treatment. To elucidate the functions of cFLIP variants, researchers constructed THP-1 cell lines overexpressing different cFLIP proteins. They discovered that only overexpressed cFLIPs, not cFLIPL, negatively regulated the selective activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. This finding indicates that the inherent limitation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation is due to the negative regulation of caspase-8 by cFLIPs, which are activated by NF-κB. Furthermore, using THP-1 cells with CFLAR gene knockout, researchers found that the absence of cFLIP significantly increases the cleavage rates of caspase-8 and caspase-1, thereby enhancing the activation of alternative inflammasomes. The specific functions of cFLIPs and TAK1 reveal a unique response of human monocytes to non-invasive pathogens, providing new insights into an alternative regulatory pathway for NLRP3 inflammasome activation..

Figure 1. cFLIPs negatively regulates the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by inhibiting the cleavage of caspase-8.
Hot KO Cells - Immunology Research
As low as ¥4980, as fast as 1 week
| Gene | Cell | Catalog # |
| ACOD1 | THP-1 | YKO-H839 |
| ADA2 | THP-1 | YKO-H084 |
| AHR | THP-1 | YKO-H692 |
| CARD8 | THP-1 | YKO-H858 |
| EGR1 | THP-1 | YKO-H127 |
| GSDMD | THP-1 | YKO-H172 |
| ISG15 | THP-1 | YKO-H722 |
| NFE2L2 | THP-1 | YKO-H083 |
| NLRP3 | THP-1 | YKO-H145 |
| PTPN11 | THP-1 | YKO-H504 |
| SIGLEC9 | THP-1 | YKO-H1064 |
| TLR1 | THP-1 | YKO-H125 |
| TLR2 | THP-1 | YKO-H101 |
| TREM2 | THP-1 | YKO-H189 |
| C3ar1 | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M209 |
| Cd180 | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M041 |
| Hmgb1 | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M031 |
| Myd88 | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M010 |
| Nfe2l2 | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M030 |
| Rheb | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M036 |
| Siglec15 | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M009 |
| Tbk1 | RAW 264.7 | YKO-M140 |
For more KO cells, welcome to consult Xiaoyuan!
Murine Macrophage Cell Line (RAW 264.7)
(Catalog No: YC-C020)
Source: RAW 264.7 cell line is a macrophage cell line established by W.C. Raschke from the ascites of a male BAB/14 mouse that developed a tumor following intraperitoneal injection of A-MuLV (Abelson murine leukemia virus).
Characteristics: This cell line is easy to propagate, has high DNA transfection efficiency, is sensitive to RNA interference, supports the replication of murine norovirus, It also has the following advantages:
1. Ease of Culture: RAW 264.7 cells grow well in conventional culture media (e.g., DMEM) and are easy to expand and passage.
2. High Responsiveness: They are highly sensitive to stimuli such as LPS and can rapidly generate a strong inflammatory response.
3. Versatility: Suitable for research in inflammation, immunity, infection, oncology, and other fields.
4. Cost-Effectiveness: Compared with other primary macrophages, RAW 264.7 cells have lower culture costs..
Application Case 2[3]: Intracellular pathogens and danger signals trigger inflammasome formation, which activates inflammatory caspases and induces pyroptosis. Both anthrax lethal toxin metalloprotease (LT) and DPP8/9 inhibitors can activate the NLRP1B inflammasome, but the molecular mechanisms underlying NLRP1B activation remain unclear. To investigate the mechanisms of NLRP1B activation, researchers conducted two genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screens in RAW 264.7 cells to identify genes whose knockout confers resistance to the DPP8/9 inhibitor Val-boroPro (VbP) or LT. The results showed that genes involved in the N-end rule proteasomal degradation pathway, including Ubr2, Ubr4, Uba6, Ube2z, and Kcmf1, were highly enriched by LT but not by VbP.
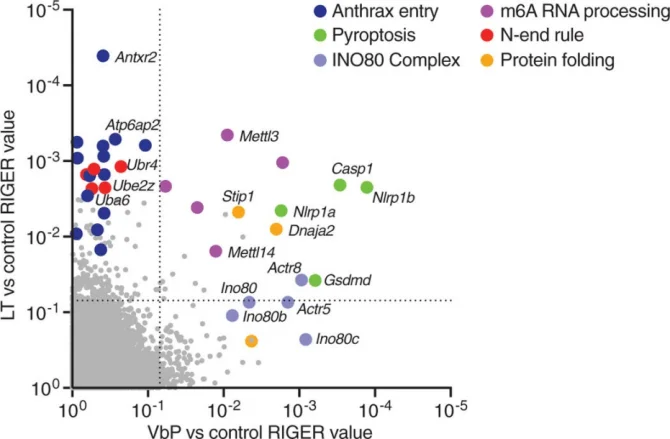
Fig. 2. Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening identifies genes involved in NLRP1B-mediated pyroptosis
Subsequently, researchers generated single- or double-gene knockout RAW 264.7 cells for UBR2, UBR4, and UBA6. They found that these knockout cells exhibited high resistance to LT, although some LT-induced cell death was still observed after 3 hours due to genetic redundancy. In contrast, no cell death or NLRP1B degradation was induced in Ubr2/4 double-knockout RAW 264.7 cells, indicating that LT induces cell death via the N-end rule proteasomal degradation pathway. This finding provides new insights into the mechanism of NLRP1B activation..
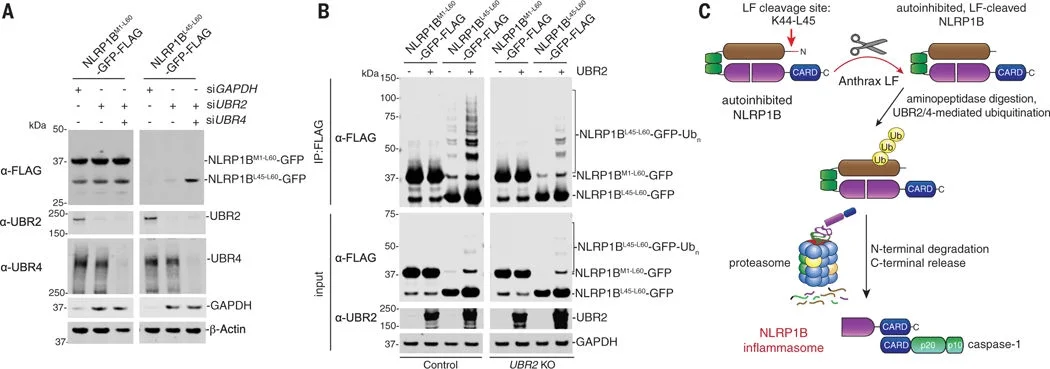
Figure 3. The cleaved N-terminus of NLRP1B induces protein degradation.
Human Leukemia T Lymphocyte Cell Line (Jurkat, Clone E6-1)
(Catalog No: YC-D012)
Source: Jurkat, Clone E6-1 was established by Schneider and derived from the peripheral blood of a 14-year-old boy with acute T-cell leukemia and is a clone of the Jurkat-FHCRC cell line (a derivative of Jurkat).
Characteristics: This cell line produces large amounts of IL-2 upon stimulation with phorbol esters and exogenous lectins or anti-T3 monoclonal antibodies (both substances are required for induction). The cells express T-cell receptors and CD3. This cell line can be used for research in immune system diseases, immunology, and immuno-oncology.
Application Case 3[4]: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and tissue damage. Recent studies have shown that variations in the KLF2 gene are associated with susceptibility to SLE. KLF2 is a transcription factor (TF) that contributes to adipogenesis, erythropoiesis, epithelial integrity, inflammation, differentiation, and migration in various types of white blood cells,including B cells and T cells.
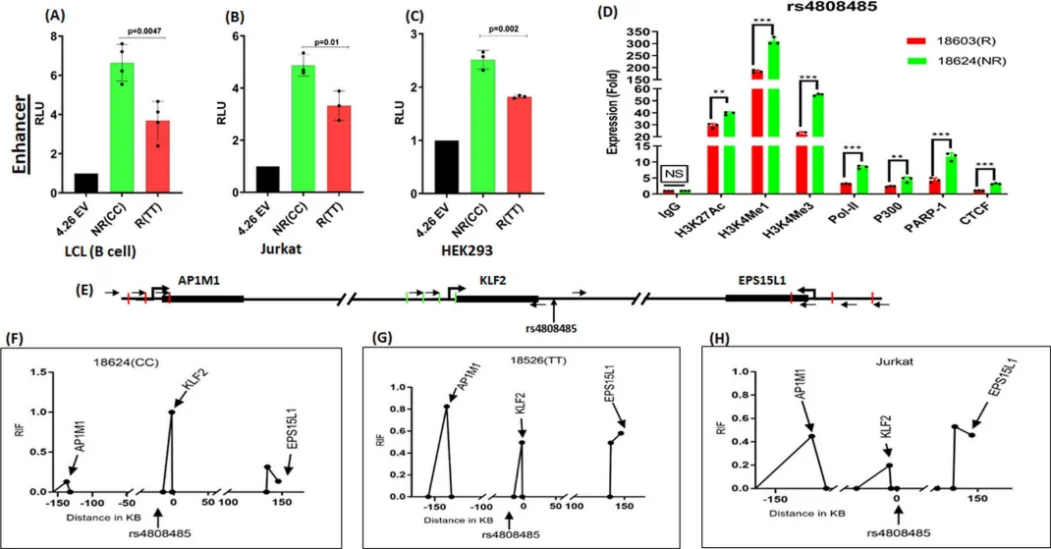
Fig. 4. Verification of allele-specific regulatory activity in the rs4808485 region
To further investigate this relationship, researchers knocked out the rs4808485 enhancer in Jurkat cells and found that the absence of rs4808485 reduced KLF2 levels and increased the levels of CASPASE1, IL-1β, and GSDMD, thereby disrupting the NLRP3 inflammasome mechanism. Compared with wild-type cells, the knockout cells also exhibited higher proliferation and cell-cycle progression. The researchers also used CRISPR/dCas9-VPR and dCas9-DNMT3A in Jurkat cells to respectively activate and repress the transcriptional activity surrounding rs4808485. VPR activation significantly increased KLF2 expression, whereas DNMT3A repression decreased KLF2 expression by approximately 30%. These findings provide new insights into the mechanisms underlying KLF2's role in SLE..
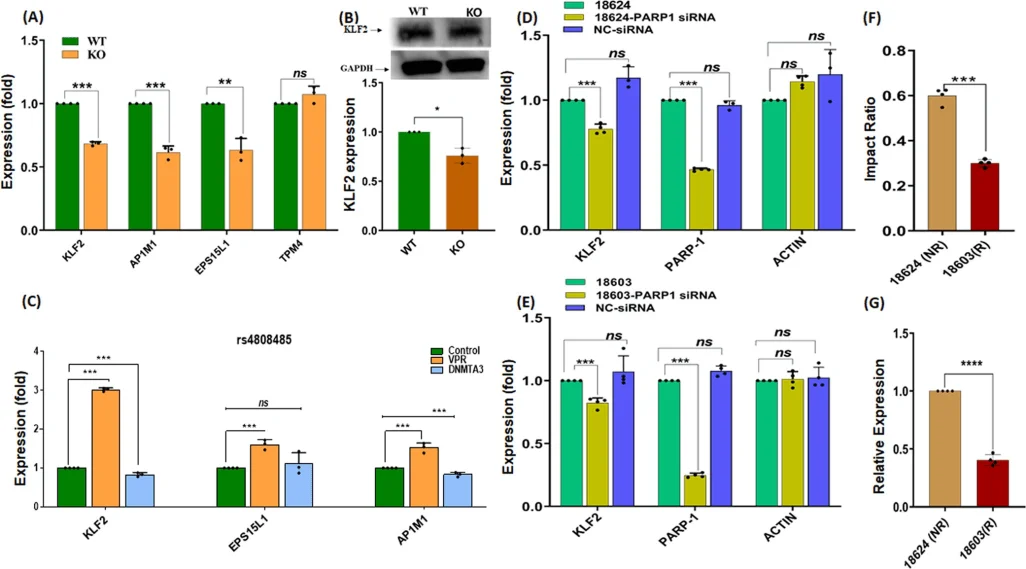
Fig. 5. The impac of CRISPR-based enhancer deletion and PARP1 knockout on target gene expression
Through the above introduction, we have learned about the important applications of the THP-1, RAW 264.7, and Jurkat Clone E6-1 cell lines in immunological research. These cellular models not only provide powerful tools for the study of immune mechanisms but also offer potential therapeutic targets for related diseases.
Ubigene can provide gene editing (KO/KI/PM) and stable transfer customization services for immune research-related cells. Consultations are welcome!!
Reference:
[1]Pardi N, Hogan MJ, Porter FW, Weissman D. mRNA vaccines - a new era in vaccinology. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Apr;17(4):261-279. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.243.
[2]Gao Y, Yu S, Chen M, Wang X, Pan L, Wei B, Meng G. cFLIPS regulates alternative NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human monocytes. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Oct;20(10):1203-1215. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01077-y.
[3]Chui AJ, Okondo MC, Rao SD, Gai K, Griswold AR, Johnson DC, Ball DP, Taabazuing CY, Orth EL, Vittimberga BA, Bachovchin DA. N-terminal degradation activates the NLRP1B inflammasome. Science. 2019 Apr 5;364(6435):82-85. doi: 10.1126/science.aau1208.
[4]Singh MK, Rallabandi HR, Zhou XJ, Qi YY, Zhao ZZ, Gan T, Zhang H, Looger LL, Nath SK. KLF2 enhancer variant rs4808485 increases lupus risk by modulating inflammasome machinery and cellular homoeostasis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Jun 12;83(7):879-888. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224953.


